In today’s fast-paced digital world, understanding the core principles of marketing is crucial for any business aiming to succeed. Marketing is more than just advertising; it encompasses a wide range of activities and strategies designed to meet the needs of customers and achieve business goals. This comprehensive guide will explore the six essential marketing concepts that every marketer should know. These concepts are the foundation of effective marketing strategies and will help you navigate the complexities of the modern market.
1. Market Segmentation
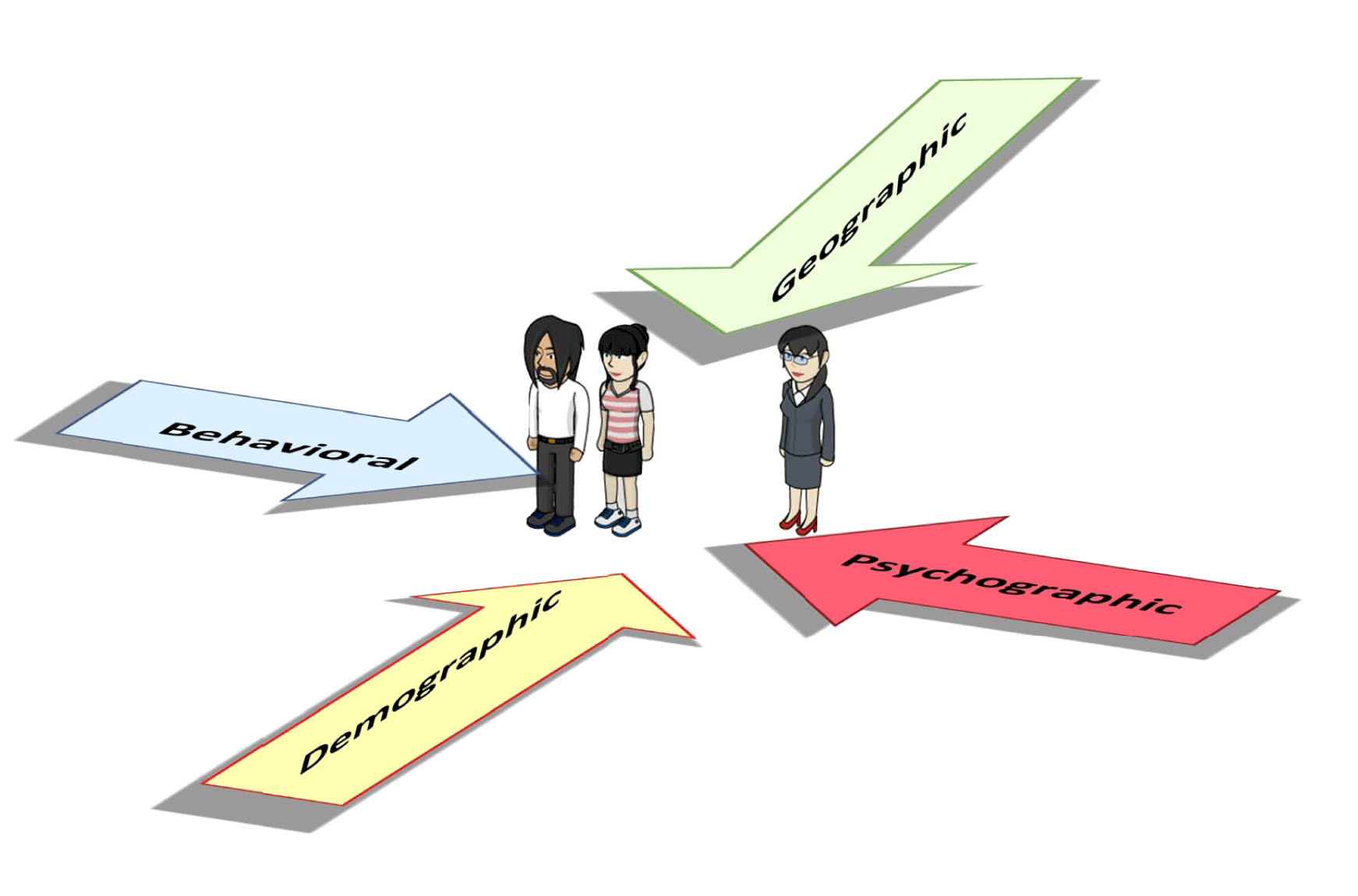
What is Market Segmentation?
Market segmentation is the process of dividing a broad consumer or business market into sub-groups of consumers (known as segments) based on some type of shared characteristics. It allows marketers to target different categories of consumers who perceive the full value of certain products and services differently from one another.
Importance of Market Segmentation
Market segmentation is essential because it helps businesses to:
- Identify and target specific groups of consumers who are most likely to respond positively to their products or services.
- Allocate marketing resources more efficiently.
- Develop more effective marketing strategies tailored to each segment’s needs and preferences.
Types of Market Segmentation
a. Demographic Segmentation
This type of segmentation divides the market based on demographic variables such as age, gender, income, education, and occupation. For example, a company selling baby products will target new parents, while a luxury car manufacturer may target high-income individuals.
Case Study: Coca-Cola’s Demographic Segmentation Coca-Cola uses demographic segmentation to target different age groups with specific products. For instance, Diet Coke is often marketed towards older consumers who are more health-conscious, while Coca-Cola Zero Sugar is targeted at younger consumers who want a sugar-free alternative without compromising taste.
b. Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation divides the market based on location. This could be by country, region, city, or even neighborhood. A fast-food chain, for instance, might tailor its menu to suit local tastes and preferences.
Case Study: McDonald’s Geographic Segmentation McDonald’s adapts its menu to cater to local tastes and preferences in different regions. For example, in India, McDonald’s offers a variety of vegetarian options and unique items like the McAloo Tikki, which are tailored to local dietary preferences.
c. Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation considers the psychological aspects of consumer behavior by dividing the market based on lifestyle, personality traits, values, opinions, and interests. For example, a fitness brand may target health-conscious consumers who value an active lifestyle.
Case Study: Nike’s Psychographic Segmentation Nike targets consumers who are passionate about fitness and sports. Their marketing campaigns often feature athletes and emphasize themes of motivation and perseverance, appealing to consumers who identify with an active and competitive lifestyle.
d. Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation divides consumers based on their behavior towards products. This includes purchasing behavior, usage rate, brand loyalty, and benefits sought. An example would be a streaming service offering different plans based on viewing habits.
Case Study: Amazon’s Behavioral Segmentation Amazon uses behavioral segmentation to recommend products based on customers’ past purchases, browsing history, and search queries. This personalized approach helps increase sales by suggesting relevant products to each user.
2. Target Marketing
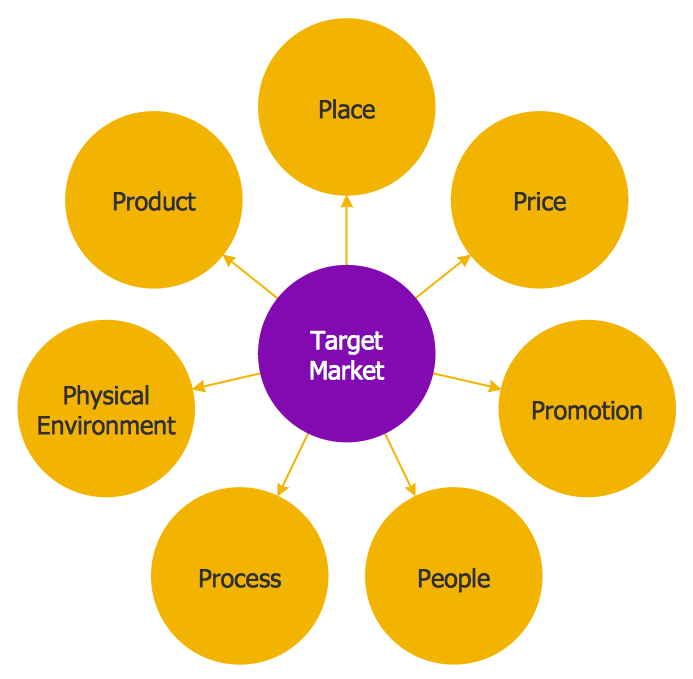
What is Target Marketing?
Target marketing involves selecting specific segments identified during market segmentation and creating tailored marketing campaigns to reach them. It ensures that marketing efforts are focused on the most promising segments, leading to better results.
Importance of Target Marketing
Target marketing is crucial because it:
- Increases the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
- Improves customer satisfaction by addressing specific needs and preferences.
- Enhances the allocation of marketing resources, maximizing return on investment (ROI).
Steps in Target Marketing
a. Identifying the Target Market
Start by analyzing market research data to identify potential segments. This involves understanding who your customers are, what they need, and how your product or service can meet those needs.
b. Evaluating Market Segments
Evaluate each segment’s potential profitability, size, accessibility, and compatibility with your brand. This will help you determine which segments are worth targeting.
c. Selecting Target Markets
Choose the most viable segments to target based on your evaluation. This selection should align with your business goals and marketing objectives.
Example: Airbnb’s Target Market Selection Airbnb identified multiple target markets, including travelers seeking affordable accommodation, hosts looking to earn extra income, and business travelers needing short-term stays. By targeting these specific segments, Airbnb was able to grow rapidly and cater to diverse customer needs.
d. Positioning the Product
Develop a positioning strategy that highlights your product’s unique value proposition to the chosen target segments. This involves creating a clear, distinctive, and desirable image of your product in the minds of consumers.
Example: Tesla’s Product Positioning Tesla positions its electric cars as high-performance, luxury vehicles that are also environmentally friendly. This positioning appeals to affluent, eco-conscious consumers who value innovation and sustainability.
3. Marketing Mix (4 Ps)
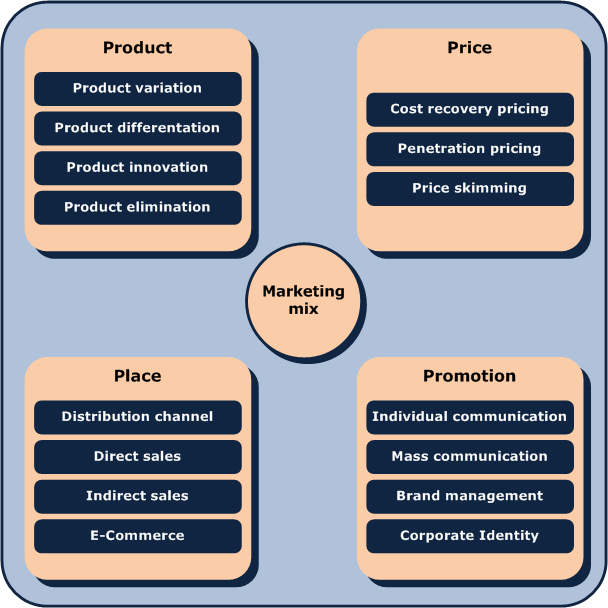
What is the Marketing Mix?
The marketing mix, often referred to as the 4 Ps, is a set of marketing tools that work together to satisfy customer needs and achieve marketing objectives. The 4 Ps include Product, Price, Place, and Promotion.
Components of the Marketing Mix
a. Product
The product refers to the goods or services offered by a business. It is the centerpiece of the marketing mix and includes aspects such as quality, design, features, branding, and packaging. Understanding what customers need and developing products that meet those needs is fundamental to successful marketing.
Example: Apple’s Product Strategy Apple focuses on creating high-quality, innovative products with sleek designs and user-friendly interfaces. Their product strategy includes a strong emphasis on brand aesthetics and premium features, which appeal to a loyal customer base.
b. Price
Price is the amount of money consumers are willing to pay for a product. Pricing strategies can significantly impact a product’s success in the market. Factors to consider include production costs, competitor pricing, perceived value, and market demand. Pricing strategies can vary from penetration pricing, skimming, competitive pricing, to value-based pricing.
Example: IKEA’s Pricing Strategy IKEA uses a value-based pricing strategy, offering affordable furniture with modern designs. By optimizing production processes and using flat-pack packaging, IKEA can keep prices low while maintaining quality.
c. Place
Place, also known as distribution, involves making the product available to consumers at the right location and time. This includes selecting distribution channels, managing logistics, and ensuring that the product reaches the end consumer efficiently. Effective distribution strategies can provide a competitive advantage by enhancing accessibility and convenience for customers.
Example: Starbucks’ Distribution Strategy Starbucks places its coffee shops in high-traffic, accessible locations such as shopping malls, urban centers, and airports. This strategic placement ensures maximum visibility and convenience for customers, driving sales and brand presence.
d. Promotion
Promotion encompasses all the activities that communicate the product’s value and persuade customers to purchase it. This includes advertising, sales promotions, public relations, direct marketing, and digital marketing. An integrated promotion strategy ensures consistent messaging across all channels and maximizes the impact of marketing efforts.
Example: Coca-Cola’s Promotion Strategy Coca-Cola uses a mix of traditional advertising (TV, radio, print) and digital marketing (social media, online ads) to promote its brand. Their campaigns often feature iconic imagery and slogans, reinforcing brand recognition and loyalty.
4. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)

What is Customer Relationship Management?
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) refers to the strategies, practices, and technologies that companies use to manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. The goal is to improve customer service, build long-term relationships, and increase sales growth.
Importance of CRM
CRM is vital for:
- Enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Providing personalized customer experiences.
- Streamlining communication and service processes.
- Gaining insights from customer data to drive strategic decisions.
Key Components of CRM
a. Data Management
Effective CRM systems collect, store, and analyze customer data, providing valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and purchase history. This data helps businesses to tailor their marketing efforts and improve customer interactions.
Example: Salesforce CRM Salesforce is a leading CRM platform that helps businesses manage customer relationships by providing tools for sales, service, marketing, and analytics. Companies like Spotify use Salesforce to manage customer interactions and deliver personalized experiences.
b. Customer Interaction
CRM focuses on managing all customer interactions across various touchpoints, including phone, email, social media, and in-person meetings. Consistent and personalized communication enhances the customer experience and fosters loyalty.
Example: Zappos’ Customer Service Zappos, an online shoe retailer, is renowned for its exceptional customer service. Their CRM approach includes personalized communication, prompt responses, and a customer-centric culture, leading to high customer satisfaction and loyalty.
c. Sales Automation
CRM systems often include sales automation tools that streamline the sales process, from lead generation to closing deals. Automation reduces manual tasks, improves efficiency, and allows sales teams to focus on building relationships and closing sales.
Example: HubSpot Sales Automation HubSpot offers sales automation tools that help businesses streamline their sales processes. Companies like Trello use HubSpot to automate follow-up emails, track interactions, and manage leads, improving sales efficiency.
d. Customer Support
Providing excellent customer support is a critical aspect of CRM. This includes responding to customer inquiries promptly, resolving issues efficiently, and maintaining a positive relationship throughout the customer journey.
Example: Amazon’s Customer Support Amazon’s customer support is known for its efficiency and responsiveness. Their CRM strategy includes a robust support system that handles inquiries through multiple channels, ensuring quick and effective resolution of customer issues.
5. Branding

What is Branding?
Branding is the process of creating a unique identity for a product or business through the use of symbols, names, logos, slogans, and designs. It differentiates a product from competitors and establishes a lasting impression in the minds of consumers.
Importance of Branding
Branding is crucial because it:
- Builds recognition and loyalty.
- Creates an emotional connection with customers.
- Enhances perceived value and credibility.
- Differentiates products in a crowded market.
Elements of Effective Branding
a. Brand Identity
Brand identity includes all the visual and verbal elements that represent the brand, such as the logo, colors, typography, and messaging. A strong brand identity creates a consistent and recognizable image across all marketing materials.
Example: Apple’s Brand Identity Apple’s brand identity is characterized by its minimalist design, sleek products, and innovative technology. The iconic Apple logo and consistent use of clean, modern aesthetics contribute to its strong brand identity.
b. Brand Positioning
Brand positioning involves defining how a brand is perceived in the minds of consumers relative to competitors. Effective positioning communicates the brand’s unique value proposition and differentiates it from the competition.
Example: Volvo’s Brand Positioning Volvo positions itself as a leader in safety and reliability. Their marketing emphasizes innovative safety features and engineering excellence, appealing to consumers who prioritize safety in their vehicle choices.
c. Brand Personality
Brand personality refers to the human characteristics associated with a brand. It helps create an emotional connection with consumers and influences their perception of the brand.
Example: Red Bull’s Brand Personality Red Bull’s brand personality is adventurous, energetic, and youthful. Their marketing campaigns often feature extreme sports and high-energy activities, resonating with consumers who identify with an active and adventurous lifestyle.
d. Brand Loyalty
Brand loyalty is the commitment of consumers to repurchase and support a brand consistently. It is achieved through positive experiences, quality products, and strong emotional connections.
Example: Starbucks’ Brand Loyalty Starbucks has built a loyal customer base through its consistent quality, personalized customer service, and rewards program. Their focus on creating a welcoming and comfortable atmosphere further enhances brand loyalty.
6. Digital Marketing

What is Digital Marketing?
Digital marketing encompasses all marketing efforts that use an electronic device or the internet. It includes various channels such as search engines, social media, email, and websites to connect with current and prospective customers.
Importance of Digital Marketing
Digital marketing is essential because it:
- Provides measurable results and data-driven insights.
- Reaches a global audience.
- Offers cost-effective marketing solutions.
- Allows for targeted and personalized marketing campaigns.
Key Components of Digital Marketing
a. Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
SEO involves optimizing a website to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs). This increases organic traffic and visibility. Effective SEO strategies include keyword research, on-page optimization, and link building.
Example: Moz’s SEO Strategy Moz, a leading SEO software company, uses content marketing and SEO to attract organic traffic. Their blog provides valuable insights and resources, helping them rank highly for relevant search terms and attract potential customers.
b. Content Marketing
Content marketing focuses on creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and engage a target audience. It aims to build trust and authority, ultimately driving profitable customer actions.
Example: HubSpot’s Content Marketing HubSpot uses content marketing to educate and engage its audience. Their blog, ebooks, webinars, and courses provide valuable information on marketing, sales, and customer service, positioning HubSpot as a thought leader in the industry.
c. Social Media Marketing
Social media marketing involves using social media platforms to promote products and engage with customers. It includes activities like posting content, running ads, and interacting with followers.
Example: Wendy’s Social Media Strategy Wendy’s is known for its witty and engaging social media presence. Their playful interactions with customers and competitors on platforms like Twitter have garnered a large following and increased brand visibility.
d. Email Marketing
Email marketing involves sending targeted emails to a group of subscribers to promote products, share news, or nurture relationships. It is a cost-effective way to reach and engage customers directly.
Example: Grammarly’s Email Marketing Grammarly uses email marketing to provide personalized writing insights and product updates to its users. Their emails are tailored to individual user behavior, increasing engagement and driving conversions.
e. Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising
PPC advertising allows businesses to display ads on search engines and other platforms, paying a fee each time the ad is clicked. It provides immediate visibility and can be highly targeted.
Example: Google’s PPC Advertising Google Ads is a popular PPC platform that allows businesses to bid on keywords and display ads in search results. Companies like eBay use Google Ads to drive targeted traffic to their website and increase sales.
f. Influencer Marketing
Influencer marketing involves partnering with influencers—individuals with a significant following on social media—to promote products. Influencers can sway the purchasing decisions of their followers, making this an effective strategy for reaching specific audiences.
Example: Daniel Wellington’s Influencer Marketing Daniel Wellington, a watch brand, leveraged influencer marketing to grow its brand. By partnering with Instagram influencers and providing discount codes, they reached a wide audience and drove significant sales.
Conclusion
Understanding and implementing the six essential marketing concepts—market segmentation, target marketing, marketing mix, customer relationship management, branding, and digital marketing—can significantly enhance your marketing efforts. Each concept plays a vital role in developing effective strategies that meet customer needs, drive business growth, and achieve competitive advantage. By mastering these fundamentals, businesses can create compelling marketing campaigns that resonate with their target audience and deliver measurable results.
Whether you’re a seasoned marketer or just starting, these concepts provide a strong foundation for navigating the ever-evolving landscape of modern marketing. Implement them thoughtfully and watch your business thrive in the dynamic and competitive market environment. Happy marketing.


thx
This is an excellent article! I appreciate the depth and clarity with which you addressed the topic. Your insights are valuable and provide a lot of useful information for readers. It’s clear that you have a strong understanding of the subject matter, and I look forward to reading more of your work. Thank you for sharing your knowledge and expertise.
There are some interesting points in time in this article but I don?t know if I see all of them center to heart. Good article , thanks and we want more! Added to FeedBurner as well